Nilevar is an oral steroid that produces moderate anabolic effects. Its side effects include acne, water-retention, hair loss and gynocomastia. It is also toxic to the liver. Despite its side effects and only moderate anabolic gains, Nilevar may be useful to athletes who suffer from joint pains, as it is especially good for relieving soreness in the joints from heavy workouts.
Nilevar (Norethandrolone): A Profile
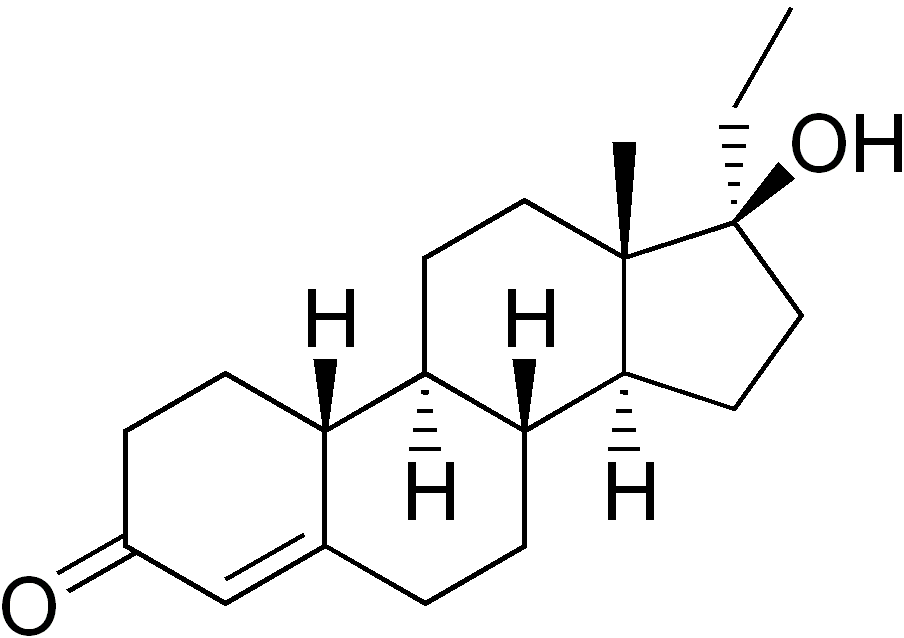
Nilevar, the brand name for Norethandrolone, is one of the earliest synthetic anabolic-androgenic steroids (AAS) developed for both medical and performance-enhancing purposes. Introduced in the 1950s, Nilevar gained recognition for its unique anabolic properties and its ability to promote muscle growth and recovery.
Chemically, Norethandrolone is derived from 19-nortestosterone, with modifications that enhance its anabolic activity while reducing androgenic effects compared to testosterone. This makes it particularly effective for athletes and bodybuilders seeking lean muscle gains without excessive water retention or significant androgenic side effects.
In medical applications, Nilevar was initially prescribed for conditions like muscle-wasting diseases, osteoporosis, and chronic illnesses that led to significant weight loss. Its ability to promote nitrogen retention and protein synthesis made it an effective tool for improving recovery and overall physical condition in patients.
In the performance-enhancing world, Nilevar has been appreciated for its capacity to build lean muscle mass, improve strength, and accelerate post-exercise recovery. However, due to its oral administration and potential hepatotoxicity, responsible use is critical. Prolonged or high-dose usage can strain the liver and disrupt hormonal balance, potentially leading to side effects such as water retention, elevated blood pressure, or mood swings.
With the advent of more advanced steroids, Nilevar has become less common in modern usage, but it remains an important milestone in the development of anabolic therapies. Today, it is primarily referenced for its historical significance and foundational role in the evolution of AAS treatments.